- The stamen is the male reproductive organ of the plant. It is composed of the anthers and filament. The anthers are what give off the sperm (pollen). They are held and located at the tip of the filament.
- The pistil (aka carpel) is the female reproduction organ of the plant. It is composed of the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is what catches the sperm (pollen). It travels down the style which directs it to the ovary. The ovary then releases the pollen to the ovule which it contains, which then initiates gametic fusion (eggs are stored in the ovule) and the creation of a seed.
- The petal is what attracts carriers of pollen to the flower to make the "exchange" parsay (pollen for nectar for example).
- Sepals (which would be between the petals in the picture) surround the petals and act as protection for the plant. They protect the plant while the flowers are in a bud state and when the flower is mature it protects from insect attack or poison.
- Double fertilization is when a sperm combines with both the egg and cell in the plant. Pollen grain has two sperm and one combines with the egg to make a zygote and the other combines with two nuclei to form the endosperm. The endosperm is the embryo's food supply and is usually composed of starch.
picture from here
| MONOCOTS | DICOTS |
| 1.Embryo with single cotyledon | 1.Embryo with two cotyledons |
| 2.Pollen with single furrow or pore | 2.Pollen with three furrows or pores |
| 3.Flower parts in multiples of three | 3.Flower parts in multiples of four or five |
| 4.Major leaf veins parallel | 4.Major leaf veins reticulated |
| 5.Stem vacular bundles scattered | 5.Stem vascular bundles in a ring |
| 6.Roots are adventitious | 6.Roots develop from radicle |
| 7.Secondary growth absent | 7.Secondary growth present |
Relatives of Mono (corn)
Wheat

Palm tree

Grass

Relatives of Di (bean)
Sunflower

Tomato plant

Pea plant

Images from here, here, here , here , and here
Translocation is the transport of nutrients and solutes throughout the plant. This is done by the phloem which carries food and minerals throughout the plant. Phloem, unlike xylem, transports materials (carbohydrates) both upwards and downwards which act as food for the plant. They are composed of sieve tubes and companion cells. The companion cells conduct sugars into the sieve tubes which transport the sugar through the phloem.

image from here
- Transpiration is the carrying of water from the roots to the leafs and released out of pores in the leaf. Its function is to give off excess water taken up for plant growth and photosynthesis.
- Turgor pressure is the pressure pushed up against the cell wall.
- Vascular tissue is made up by the xylem and phloem. By means of vascular tissue, nutrients and water are transported throughout the plant.
- Soil contributes to plant growth immensely. Soil contains the nutrients and moisture that plants need to grow and survive. Photosynthesis allows for plants to grow and is obtained through the soil.
- The casparian strip is like the guard cell of the vascular tissue. It blocks solutes and water from entering the vascular tissue and thus into being transported throughout the plant.
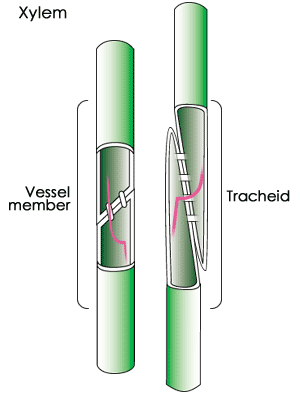
- The xylem is one of the two vascular tissues and serves the main purpose of transporting water and dissolved ions upwards throughout the plant. It's structure looks like this. Composed off a membrane and tracheids which are cells that transport water through the xylem tubes.
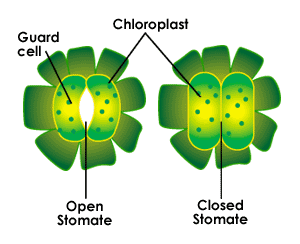
- Gas exchange is through the stomata and guard cells. The stomata are holes in the leaf epidermis that allows gas exchange while the guard cells protects the stomata by closing and opening by swelling. There are two guard cells to every stoma. So the stomata is the hole and the guard cells allow for things to enter or leave the stomata.